|
|
PathReuseDecider 是lanefollow 场景下,所调用的第 2 个 task,它的作用主要是换道时:
- 根据横纵向跟踪偏差,来决策是否需要重新规划轨迹;
- 如果横纵向跟踪偏差,则根据上一时刻的轨迹生成当前周期的轨迹,以尽量保持轨迹的一致性
Apollo Planning决策规划系列文章:
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (1):Scenario选择
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (2):Scenario执行
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (3):stage执行
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (4):Stage逻辑详解
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (5):规划算法流程介绍
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (6):LaneChangeDecider
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (7): PathReuseDecider
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (8): PathLaneBorrowDecider
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (9): PathBoundsDecider
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (10):PiecewiseJerkPathOptimizer
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (11): PathAssessmentDecider
自动驾驶Player:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (12): PathDecider
算法详细介绍系列文章:
自动驾驶Player:Apollo决策规划算法Planning : 路径规划Piecewise Jerk Path Optimizer的python实现
后续apollo规划算法完整解析会在下面专栏进行更新:
正文如下:
一、概述
PathReuseDecider 是lanefollow 场景下,所调用的第 2 个 task,它的作用主要是换道时:
- 根据横纵向跟踪偏差,来决策是否需要重新规划轨迹;
- 如果横纵向跟踪偏差,则根据上一时刻的轨迹生成当前周期的轨迹,以尽量保持轨迹的一致性
二、PathReuseDecider的流程图与概述:
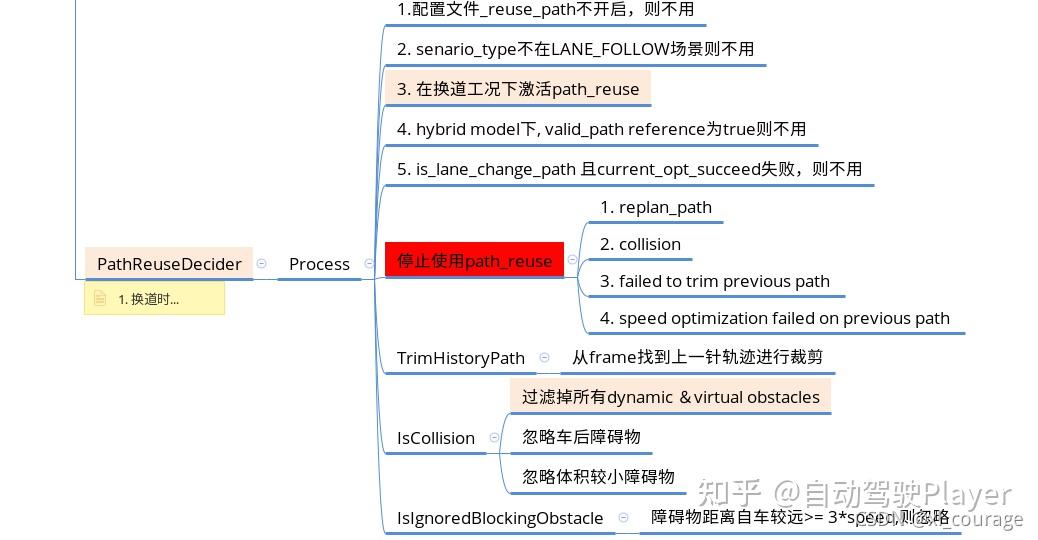
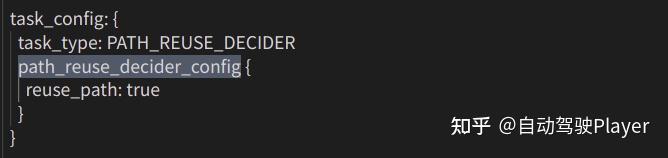
1、使用该功能前首先应该打开配置:
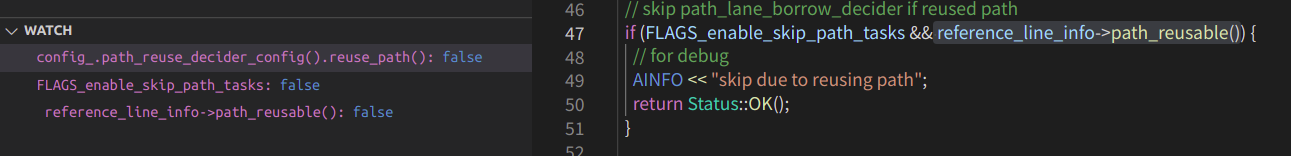
2、在之后进行的每个task,首先要进行检查配置是否打开,并读取PathReuseDecider的结果确定是否要进行之后的task完成新的决策规划任务:
接下来的lane_borrow_decider为例,在task进行的开始阶段,进行以下判断:
三、PathReuseDecider的具体逻辑如下:
1、PublicRoadPlanner 的 LaneFollowStage 配置了以下几个task 来实现具体的规划逻辑,PathReuseDecider 是第二个task:
scenario_type: LANE_FOLLOW
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
stage_config: {
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
enabled: true
task_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
task_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
task_type: ST_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
task_type: SPEED_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: RSS_DECIDER
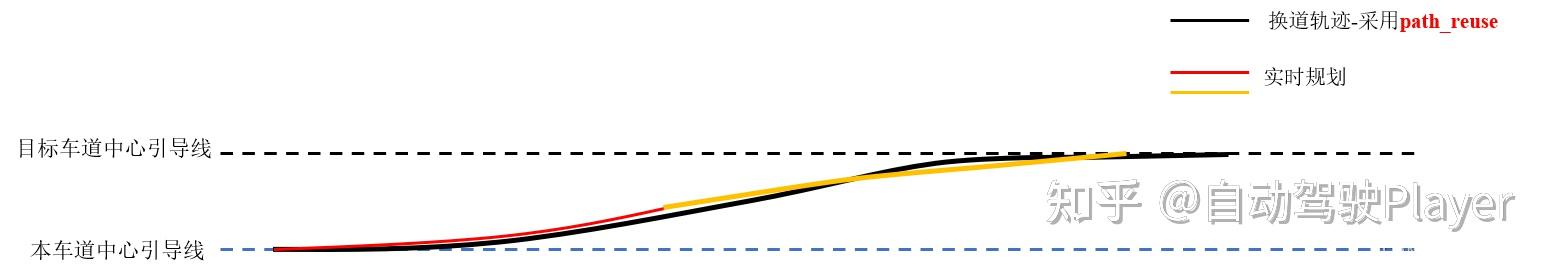
}2、 使用path_reuse的好处:
黑色轨迹为采用path_reuse,可以看到整个换道过程,轨迹完全一致; 红色、黄色轨迹为重新规划轨迹并采用trajectory_stitcher 拼接。
可以看到在轨迹拼接处以及整体轨迹可能出现不连贯不平滑的情况,可能会影响控制的平顺性:
3、PathReuseDecider 只对外暴露了Process() 一个接口,它的主要逻辑如下:
(1)当前处于非LaneFollow_Scenario场景,置位false
(2)当前未处于IN_CHANGE_LANE状态,置位false;
(3)如果存在可变车道,且已经完成换道轨迹生成,则置位false;
(4)前一时刻采用path_reuse, 若轨迹重规划、轨迹与静态障碍物发生碰撞、轨迹长度过短以及纵向求解失败,则置位false;
(5)只有前方静止障碍物走开(或大于阈值)、纵向求解成功、未与静态障碍物发生碰撞且轨迹长度大于阈值,才可置位true;
Status PathReuseDecider::Process(Frame* const frame,
ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
// Sanity checks.
CHECK_NOTNULL(frame);
CHECK_NOTNULL(reference_line_info);
if (!Decider::config_.path_reuse_decider_config().reuse_path()) {
ADEBUG << &#34;skipping reusing path: conf&#34;;
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(false);
return Status::OK();
}
// skip path reuse if not in LANE_FOLLOW_SCENARIO
const auto scenario_type = injector_->planning_context()
->planning_status()
.scenario()
.scenario_type();
if (scenario_type != ScenarioConfig::LANE_FOLLOW) {
ADEBUG << &#34;skipping reusing path: not in LANE_FOLLOW scenario&#34;;
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(false);
return Status::OK();
}
// active path reuse during change_lane only
auto* lane_change_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_change_lane();
ADEBUG << &#34;lane change status: &#34; << lane_change_status->ShortDebugString();
// skip path reuse if not in_change_lane
if (lane_change_status->status() != ChangeLaneStatus::IN_CHANGE_LANE &&
!FLAGS_enable_reuse_path_in_lane_follow) {
ADEBUG << &#34;skipping reusing path: not in lane_change&#34;;
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(false);
return Status::OK();
}
// for hybrid model: skip reuse path for valid path reference
const bool valid_model_output =
reference_line_info->path_data().is_valid_path_reference();
if (valid_model_output) {
ADEBUG << &#34;skipping reusing path: path reference is valid&#34;;
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(false);
return Status::OK();
}
/*count total_path_ when in_change_lane && reuse_path*/
++total_path_counter_;
/*reuse path when in non_change_lane reference line or
optimization succeeded in change_lane reference line
*/
bool is_change_lane_path = reference_line_info->IsChangeLanePath();
if (is_change_lane_path && !lane_change_status->is_current_opt_succeed()) {
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(false);
ADEBUG << &#34;reusable_path_counter[&#34; << reusable_path_counter_
<< &#34;] total_path_counter[&#34; << total_path_counter_ << &#34;]&#34;;
ADEBUG << &#34;Stop reusing path when optimization failed on change lane path&#34;;
return Status::OK();
}
// stop reusing current path:
// 1. replan path
// 2. collision
// 3. failed to trim previous path
// 4. speed optimization failed on previous path
bool speed_optimization_successful = false;
const auto& history_frame = injector_->frame_history()->Latest();
if (history_frame) {
const auto history_trajectory_type =
history_frame->reference_line_info().front().trajectory_type();
speed_optimization_successful =
(history_trajectory_type != ADCTrajectory::SPEED_FALLBACK);
}
// const auto history_trajectory_type = injector_->FrameHistory()s
// ->Latest()
// ->reference_line_info()
// .front()
// .trajectory_type();
if (path_reusable_) {
if (!frame->current_frame_planned_trajectory().is_replan() &&
speed_optimization_successful && IsCollisionFree(reference_line_info) &&
TrimHistoryPath(frame, reference_line_info)) {
ADEBUG << &#34;reuse path&#34;;
++reusable_path_counter_; // count reusable path
} else {
// stop reuse path
ADEBUG << &#34;stop reuse path&#34;;
path_reusable_ = false;
}
} else {
// F -> T
auto* mutable_path_decider_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_path_decider();
static constexpr int kWaitCycle = -2; // wait 2 cycle
const int front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter =
mutable_path_decider_status->front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter();
const bool ignore_blocking_obstacle =
IsIgnoredBlockingObstacle(reference_line_info);
ADEBUG << &#34;counter[&#34; << front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter
<< &#34;] IsIgnoredBlockingObstacle[&#34; << ignore_blocking_obstacle << &#34;]&#34;;
// stop reusing current path:
// 1. blocking obstacle disappeared or moving far away
// 2. trimming successful
// 3. no statical obstacle collision.
if ((front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter <= kWaitCycle ||
ignore_blocking_obstacle) &&
speed_optimization_successful && IsCollisionFree(reference_line_info) &&
TrimHistoryPath(frame, reference_line_info)) {
// enable reuse path
ADEBUG << &#34;reuse path: front_blocking_obstacle ignorable&#34;;
path_reusable_ = true;
++reusable_path_counter_;
}
}
reference_line_info->set_path_reusable(path_reusable_);
ADEBUG << &#34;reusable_path_counter[&#34; << reusable_path_counter_
<< &#34;] total_path_counter[&#34; << total_path_counter_ << &#34;]&#34;;
return Status::OK();
}
4、当path_reusable置位后,后续的task会跳过处理的过程:
// skip path_lane_borrow_decider if reused path
if (FLAGS_enable_skip_path_tasks && reference_line_info->path_reusable()) {
// for debug
AINFO << &#34;skip due to reusing path&#34;;
return Status::OK();
}
5、一旦path_reusable置位,则使用上一周期轨迹生成当前周期的规划轨迹:
bool PathReuseDecider::TrimHistoryPath(
Frame* frame, ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
...
//找到上一帧轨迹的起始点
const common::TrajectoryPoint history_planning_start_point =
history_frame->PlanningStartPoint();
common::PathPoint history_init_path_point =
history_planning_start_point.path_point();
//当前周期规划的起点
const common::TrajectoryPoint planning_start_point =
frame->PlanningStartPoint();
common::PathPoint init_path_point = planning_start_point.path_point();
const DiscretizedPath& history_path =
history_frame->current_frame_planned_path();
DiscretizedPath trimmed_path;
common::SLPoint adc_position_sl;
// 依据当前自车所处位置,计算其frenet坐标
GetADCSLPoint(reference_line, &adc_position_sl);
size_t path_start_index = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < history_path.size(); ++i) {
// 找到上周期轨迹规划的起点索引
if (history_path.s() > 0) {
path_start_index = i;
break;
}
}
// get current s=0
common::SLPoint init_path_position_sl;
//计算当前轨迹的起点的在上周期reference_line中的frenet坐标
reference_line.XYToSL(init_path_point, &init_path_position_sl);
bool inserted_init_point = false;
//匹配当前规划起点位置,裁剪该点之后的轨迹
for (size_t i = path_start_index; i < history_path.size(); ++i) {
common::SLPoint path_position_sl;
common::math::Vec2d path_position = {history_path.x(),
history_path.y()};
reference_line.XYToSL(path_position, &path_position_sl);
double updated_s = path_position_sl.s() - init_path_position_sl.s();
// insert init point
if (updated_s > 0 && !inserted_init_point) {
trimmed_path.emplace_back(init_path_point);
trimmed_path.back().set_s(0);
inserted_init_point = true;
}
trimmed_path.emplace_back(history_path);
trimmed_path.back().set_s(updated_s);
}
ADEBUG << &#34;trimmed_path[0]: &#34; << trimmed_path.front().s();
ADEBUG << &#34;[END] trimmed_path.size(): &#34; << trimmed_path.size();
if (!NotShortPath(trimmed_path)) {
ADEBUG << &#34;short path: &#34; << trimmed_path.size();
return false;
}
// 更新规划后的路径信息
auto path_data = reference_line_info->mutable_path_data();
ADEBUG << &#34;previous path_data size: &#34; << history_path.size();
path_data->SetReferenceLine(&reference_line);
ADEBUG << &#34;previous path_data size: &#34; << path_data->discretized_path().size();
path_data->SetDiscretizedPath(DiscretizedPath(std::move(trimmed_path)));
ADEBUG << &#34;not short path: &#34; << trimmed_path.size();
ADEBUG << &#34;current path size: &#34;
<< reference_line_info->path_data().discretized_path().size();
return true;
}
6、在判断是否 path_reusable时,会调用IsCollisionFree 判断静态目标是否安全:
bool PathReuseDecider::IsCollisionFree(
ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
const ReferenceLine& reference_line = reference_line_info->reference_line();
static constexpr double kMinObstacleArea = 1e-4;
const double kSBuffer = 0.5;
static constexpr int kNumExtraTailBoundPoint = 21;
static constexpr double kPathBoundsDeciderResolution = 0.5;
// current vehicle sl position
common::SLPoint adc_position_sl;
GetADCSLPoint(reference_line, &adc_position_sl);
// current obstacles
std::vector<Polygon2d> obstacle_polygons;
for (auto obstacle :
reference_line_info->path_decision()->obstacles().Items()) {
// filtered all non-static objects and virtual obstacle
if (!obstacle->IsStatic() || obstacle->IsVirtual()) {
if (!obstacle->IsStatic()) {
ADEBUG << &#34;SPOT a dynamic obstacle&#34;;
}
if (obstacle->IsVirtual()) {
ADEBUG << &#34;SPOT a virtual obstacle&#34;;
}
continue;
}
const auto& obstacle_sl = obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary();
// Ignore obstacles behind ADC
if ((obstacle_sl.end_s() < adc_position_sl.s() - kSBuffer) ||
// Ignore too small obstacles.
(obstacle_sl.end_s() - obstacle_sl.start_s()) *
(obstacle_sl.end_l() - obstacle_sl.start_l()) <
kMinObstacleArea) {
continue;
}
obstacle_polygons.push_back(
Polygon2d({Vec2d(obstacle_sl.start_s(), obstacle_sl.start_l()),
Vec2d(obstacle_sl.start_s(), obstacle_sl.end_l()),
Vec2d(obstacle_sl.end_s(), obstacle_sl.end_l()),
Vec2d(obstacle_sl.end_s(), obstacle_sl.start_l())}));
}
if (obstacle_polygons.empty()) {
return true;
}
const auto& history_frame = injector_->frame_history()->Latest();
if (!history_frame) {
return false;
}
const DiscretizedPath& history_path =
history_frame->current_frame_planned_path();
// path end point
common::SLPoint path_end_position_sl;
common::math::Vec2d path_end_position = {history_path.back().x(),
history_path.back().y()};
reference_line.XYToSL(path_end_position, &path_end_position_sl);
for (size_t i = 0; i < history_path.size(); ++i) {
common::SLPoint path_position_sl;
common::math::Vec2d path_position = {history_path.x(),
history_path.y()};
reference_line.XYToSL(path_position, &path_position_sl);
if (path_end_position_sl.s() - path_position_sl.s() <=
kNumExtraTailBoundPoint * kPathBoundsDeciderResolution) {
break;
}
if (path_position_sl.s() < adc_position_sl.s() - kSBuffer) {
continue;
}
const auto& vehicle_box =
common::VehicleConfigHelper::Instance()->GetBoundingBox(
history_path);
std::vector<Vec2d> ABCDpoints = vehicle_box.GetAllCorners();
for (const auto& corner_point : ABCDpoints) {
// For each corner point, project it onto reference_line
common::SLPoint curr_point_sl;
if (!reference_line.XYToSL(corner_point, &curr_point_sl)) {
AERROR << &#34;Failed to get the projection from point onto &#34;
&#34;reference_line&#34;;
return false;
}
auto curr_point = Vec2d(curr_point_sl.s(), curr_point_sl.l());
// Check if it&#39;s in any polygon of other static obstacles.
for (const auto& obstacle_polygon : obstacle_polygons) {
if (obstacle_polygon.IsPointIn(curr_point)) {
// for debug
ADEBUG << &#34;s distance to end point:&#34; << path_end_position_sl.s();
ADEBUG << &#34;s distance to end point:&#34; << path_position_sl.s();
ADEBUG << &#34;[&#34; << i << &#34;]&#34;
<< &#34;, history_path.x(): &#34; << std::setprecision(9)
<< history_path.x() << &#34;, history_path.y()&#34;
<< std::setprecision(9) << history_path.y();
ADEBUG << &#34;collision:&#34; << curr_point.x() << &#34;, &#34; << curr_point.y();
Vec2d xy_point;
reference_line.SLToXY(curr_point_sl, &xy_point);
ADEBUG << &#34;collision:&#34; << xy_point.x() << &#34;, &#34; << xy_point.y();
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「自动驾驶 Player」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:Apollo Planning决策规划代码详细解析 (7): PathReuseDecider |
|